Efficient PRAM and Practical GPU Algorithms for Large Polygon Clipping with Degenerate Cases
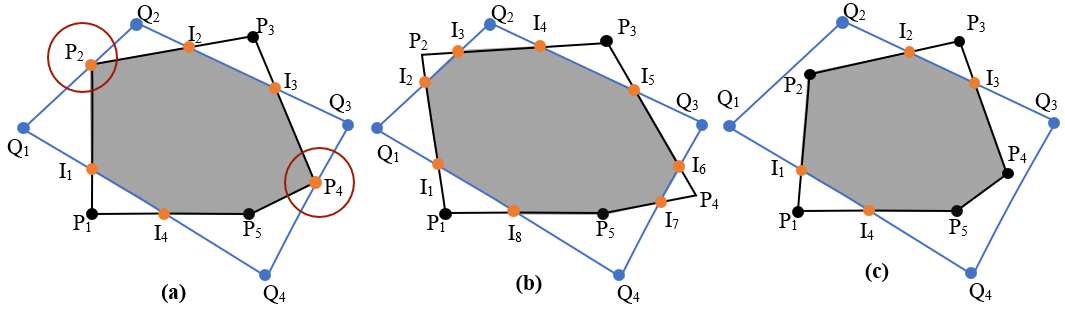
Polygonal geometric operations are fundamental in domains such as Computer Graphics, Computer-Aided Design, and Geographic Information Systems. Handling degenerate cases in such operations is important when real-world spatial data are used. The popular Greiner-Hormann (GH) clipping algorithm does not handle such cases properly without perturbing vertices leading to inaccuracies and ambiguities. In this work, we parallelize the O(n2 )-time general polygon clipping algorithm by Foster et al. which can handle degenerate cases without perturbation. Our CREW PRAM algorithm can perform clipping in O(log n) time using n + k number of processors with simple polygons, where n is the number of input edges and k is the number of edge intersections. For efficient GPU implementation, we employ three effective filters which have not been used in prior work on polygon clipping: 1) Commonminimum-bounding-rectangle filter, 2) Count-based filter, and 3) Line-segment-minimum-bounding-rectangle filter. They drastically reduce O(n2 ) candidate edge pairs comparisons by 80%- 99%, leading to significantly faster parallel execution. In our experiments, C++ CUDA-based implementation yields up to 40X speedup over real-world datasets, processing two polygons with a total of 174K vertices on an Nvidia Quadro RTX 5000 GPU compared to the sequential Foster’s algorithm running on an Intel Xeon Silver 4210R CPU.
Go to PaperExtending segment tree for polygon clipping and parallelizing using OpenMP and OpenACC compiler directives
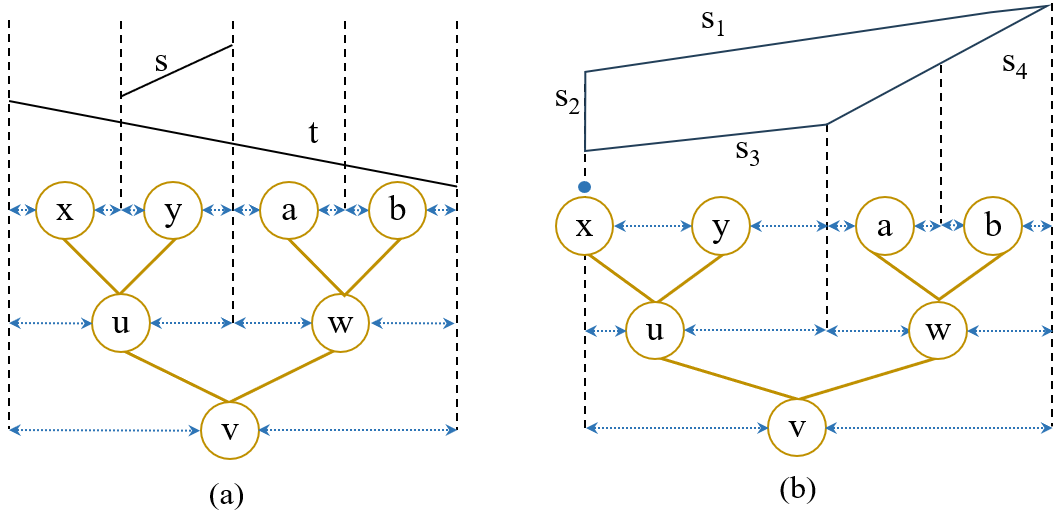
- The first work to extend a segment tree data structure for polygon clipping leveraging Chaselle’s rules.
- Parallelized segment tree construction including augmented data structures and line segment intersection finding using OpenMP directives.
- Presented a performance analysis including parallel kernel offloading using OpenACC.
Approximate Nearest Neighbor Similarity Search for Large Polygonal and Trajectory Datasets
- Developed uniform grid-based and quad tree-based polygon encoding techniques to encode a polygon into a feature vector.
- Presented a workflow leveraging Jaccard distance to find similar shapes from a large reference dataset employing a HNSW graph for fast searching. Python was used for implementations.
EScooterLab - A Programmable and Participatory Sensing Testbed using Micromobility Vehicles
- Developed a Map tool employing an ArcGIS base map to visualize scooter trip trajectories and their sensor data using JavaScript.
- Designed and contributed to develop a PHP backend application to manage researchers and experiments using Laravel framework.
ECS6253: Survey-based Term Project

Spatial and spatiotemporal data models and operations are the building blocks of spatial analysis. Geospatial analysis algorithms are compute-intensive and large volumes of such data make this task more challenging. Traditional databases cannot handle these operations and high volumes of data efficiently. Polygon is a basic data model used in this research landscape. This study focuses on efficient parallel data structures and algorithms that are used to store and manipulate polygonal data in geospatial analysis. This work presents data structures specialized for efficient processing with spatial and spatiotemporal data, serial and parallel algorithms that are used for polygon clipping over spatial data and range queries over spatiotemporal data.
Go to Project